{
event: "article_read",
name: `The Importance of C-peptide in Autoimmune T1D `,
author: ``,
tags: `Infographic | Management | Pathophysiology`,
publication_date: ``,
interaction_type: "content"
}
- Resource
- BR1DGE
- Infographic
- Management
- Pathophysiology
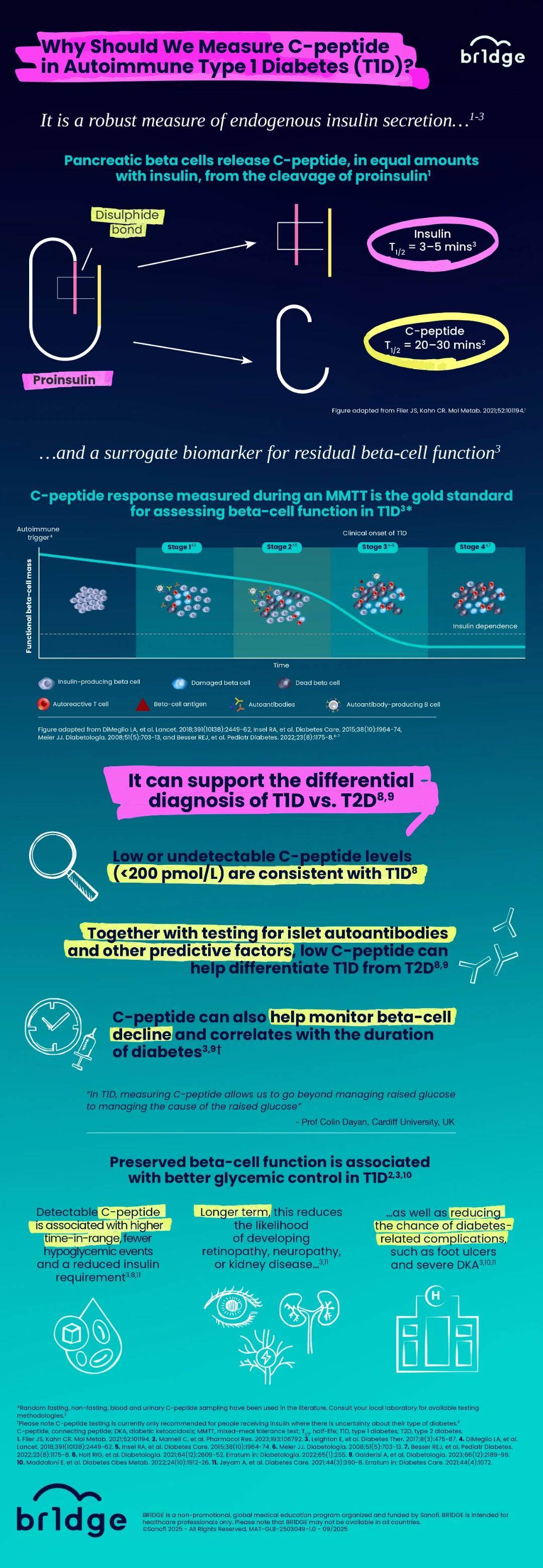
The Importance of C-peptide in Autoimmune T1D
An infographic summarising C-peptide, a key biomarker of beta-cell function.
Learning Objectives
- Understand that C-peptide is a byproduct of insulin synthesis
- Recognize C-peptide's role in understanding disease status in T1D
- Appreciate C-peptide's potential as a diagnostic and prognostic tool
Summary
C-peptide is a key tool in autoimmune type 1 diabetes (T1D) management. It aids diagnosis, disease monitoring, and is a key biomarker for beta-cell function and endogenous insulin secretion. C-peptide measurement during a mixed-meal tolerance test is the gold standard for assessing beta-cell function. Residual C-peptide predicts positive outcomes, fewer diabetes-related complications, and improved glycemic control, meaning C-peptide can potentially guide early interventions to delay or prevent the clinical onset of T1D.
MAT-GLB-2503049 - 1.0 - 09/2025
Similar Content